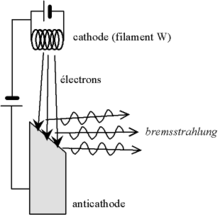
پرتوی ایکس
پرتو ایکس یا اشعه ایکس (اشعه رونتگن) نوعی از امواج الکترومغناطیس با طول موج حدود ۱۰ تا ۱۰-۲ آنگستروم است که در بلورشناسی و عکسبرداری از اعضای داخلی بدن و عکسبرداری از درون اشیای جامد و به عنوان یکی از روشهای تست غیرمخرب در تشخیص نقصهای موجود در اشیای ساخته شده (مثلاً در لولههاو...) کاربرد دارد.
محتویات
[نهفتن]- ۱ تاریخچه
- ۲ انواع پرتو ایکس
- ۳ روشهای تولید
- ۴ ایمنی
- ۵ منابع
- ۶ پیوندهای مفید به بیرون
- ۷ جستارهای وابسته
بقه و متن کامل در ادامه مطالب...
پرتوی ایکس
پرتو ایکس یا اشعه ایکس (اشعه رونتگن) نوعی از امواج الکترومغناطیس با طول موج حدود ۱۰ تا ۱۰-۲ آنگستروم است که در بلورشناسی و عکسبرداری از اعضای داخلی بدن و عکسبرداری از درون اشیای جامد و به عنوان یکی از روشهای تست غیرمخرب در تشخیص نقصهای موجود در اشیای ساخته شده (مثلاً در لولههاو...) کاربرد دارد.
محتویات
[نهفتن]- ۱ تاریخچه
- ۲ انواع پرتو ایکس
- ۳ روشهای تولید
- ۴ ایمنی
- ۵ منابع
- ۶ پیوندهای مفید به بیرون
- ۷ جستارهای وابسته
بقیه و متن کامل در ادامه مطالب...
دید کلی با توجه به اینکه اشعه گاما دارای تشعشع الکترومغناطیسی میباشد، آن فاقد بار و جرم سکون است. اشعه گاما موجب برهمکنشهای کولنی نمیگردد و لذا آنها برخلاف ذرات باردار بطور پیوسته انرژی از دست نمیدهند. معمولا اشعه گاما تنها یک یا چند برهمکنش اتفاقی با الکترونها یا هستههای اتمهای ماده جذب کننده احساس میکند. در این برهمکنشها اشعه گاما یا بطور کامل ناپدید می گردد یا انرژی آن بطور قابل ملاحظهای تغییر مییابد. اشعه گاما دارای بردهای مجزا نیست، به جای آن ، شدت یک باری که اشعه گاما بطور پیوسته با عبور آن از میان ماده مطابق قانون نمایی جذب کاهش مییابد
بقیه و کامل مطلب در ادامه مطالب...
دانلود در ادامه مطالب...
سری فوریه، روشی در ریاضیات میباشد که به وسیله آن، هر تابع متناوبی به صورت جمعی از توابع سینوس و کسینوس میتواند نوشته شود. نام این قضیه به اسم ریاضیدان فرانسوی، ژوزف فوریه ثبت شده است. هدف از این کار، نمایش توابع در دامنه فرکانس میباشد.
محتویات
[نهفتن]بقیه و متن کامل مقاله در ادامه مطالب...
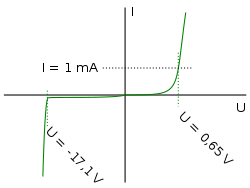
Zener diode
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding reliable references. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (December 2009) |
A Zener diode is a type of diode that permits current not only in the forward direction like a normal diode, but also in the reverse direction if the voltage is larger than the breakdown voltage known as "Zener knee voltage" or "Zener voltage". The device was named after Clarence Zener, who discovered this electrical property.
A conventional solid-state diode will not allow significant current if it is reverse-biased below its reverse breakdown voltage. When the reverse bias breakdown voltage is exceeded, a conventional diode is subject to high current due to avalanche breakdown. Unless this current is limited by circuitry, the diode will be permanently damaged due to overheating. In case of large forward bias (current in the direction of the arrow), the diode exhibits a voltage drop due to its junction built-in voltage and internal resistance. The amount of the voltage drop depends on the semiconductor material and the doping concentrations.
A Zener diode exhibits almost the same properties, except the device is specially designed so as to have a greatly reduced breakdown voltage, the so-called Zener voltage. By contrast with the conventional device, a reverse-biased Zener diode will exhibit a controlled breakdown and allow the current to keep the voltage across the Zener diode close to the Zener breakdown voltage. For example, a diode with a Zener breakdown voltage of 3.2 V will exhibit a voltage drop of very nearly 3.2 V across a wide range of reverse currents. The Zener diode is therefore ideal for applications such as the generation of a reference voltage (e.g. for an amplifier stage), or as a voltage stabilizer for low-current applications.
The Zener diode's operation depends on the heavy doping of its p-n junction allowing electrons to tunnel from the valence band of the p-type material to the conduction band of the n-type material. In the atomic scale, this tunneling corresponds to the transport of valence band electrons into the empty conduction band states; as a result of the reduced barrier between these bands and high electric fields that are induced due to the relatively high levels of dopings on both sides.[1] The breakdown voltage can be controlled quite accurately in the doping process. While tolerances within 0.05% are available, the most widely used tolerances are 5% and 10%. Breakdown voltage for commonly available zener diodes can vary widely from 1.2 volts to 200 volts.
Another mechanism that produces a similar effect is the avalanche effect as in the avalanche diode. The two types of diode are in fact constructed the same way and both effects are present in diodes of this type. In silicon diodes up to about 5.6 volts, the Zener effect is the predominant effect and shows a marked negative temperature coefficient. Above 5.6 volts, the avalanche effect becomes predominant and exhibits a positive temperature coefficient.[1] In a 5.6 V diode, the two effects occur together and their temperature coefficients neatly cancel each other out, thus the 5.6 V diode is the component of choice in temperature-critical applications. Modern manufacturing techniques have produced devices with voltages lower than 5.6 V with negligible temperature coefficients, but as higher voltage devices are encountered, the temperature coefficient rises dramatically. A 75 V diode has 10 times the coefficient of a 12 V diode.
All such diodes, regardless of breakdown voltage, are usually marketed under the umbrella term of "Zener diode".
Contents
[hide]بقیه و متن کامل مقاله در ادامه مطالب...
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both. Electronic filters can be:
- passive or active
- analog or digital
- high-pass, low-pass, bandpass, band-reject (band reject; notch), or all-pass.
- discrete-time (sampled) or continuous-time
- linear or non-linear
- infinite impulse response (IIR type) or finite impulse response (FIR type)
The most common types of electronic filters are linear filters, regardless of other aspects of their design. See the article on linear filters for details on their design and analysis.
Contents
[hide]- 1 History
- 2 Classification by technology
- 3 The transfer function
- 4 Classification by topology
- 5 Classification by design methodology
- 6 See also
- 7 External links and references
بقیه و متن کامل مقاله در ادامه ی مطالب...
Electric power distribution
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding reliable references. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (January 2008) |
Electricity distribution is the final stage in the delivery (before retail) of electricity to end users. A distribution system's network carries electricity from the transmission system and delivers it to consumers. Typically, the network would include medium-voltage (less than 50 kV) power lines, electrical substations and pole-mounted transformers, low-voltage (less than 1 kV) distribution wiring and sometimes electricity meters.
Contents
[hide]- 1 Modern distribution systems
- 2 History
- 3 Distribution network configurations
- 4 Distribution industry
- 5 See also
- 6 References
- 7 External links
- 8 Further reading
بقیه و متن کامل مقاله در ادامه مطالب...
Electrical conductor
|
|
This article does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (January 2009) |
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is a material which contains movable electric charges. In metallic conductors, such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons (see electrical conduction). Positive charges may also be mobile in the form of atoms in a lattice that are missing electrons (known as holes), or in the form of ions, such as in the electrolyte of a battery. Insulators are non-conducting materials with fewer mobile charges, which resist the flow of electric current.
All conductors contain electric charges which will move when an electric potential difference (measured in volts) is applied across separate points on the material. This flow of charge (measured in amperes) is what is meant by electric current. In most materials, the direct current is proportional to the voltage (as determined by Ohm's law), provided the temperature remains constant and the material remains in the same shape and state.
Most familiar conductors are metallic. Copper is the most common material used for electrical wiring. Silver is the best conductor, but is expensive. Because it does not corrode, gold is used for high-quality surface-to-surface contacts. However, there are also many non-metallic conductors, including graphite, solutions of salts, and all plasmas. There are even conductive polymers. See electrical conduction for more information on the physical mechanism for charge flow in materials.
All non-superconducting materials offer some resistance and warm up when a current flows. Thus, proper design of an electrical conductor takes into account the temperature that the conductor needs to be able to endure without damage, as well as the quantity of electric current. The motion of charges also creates an electromagnetic field around the conductor that exerts a mechanical radial squeezing force on the conductor. A conductor of a given material and volume (length × cross-sectional area) has no real limit to the current it can carry without being destroyed as long as the heat generated by the resistive loss is removed and the conductor can withstand the radial forces. This effect is especially critical in printed circuits, where conductors are relatively small and close together, and inside an enclosure: the heat produced, if not properly removed, can cause fusing (melting) of the tracks.
Thermal and electrical conductivity often go together. For instance, most metals are both electrical and thermal conductors. However, some materials are practical electrical conductors without being good thermal conductors.
Contents
[hide]بقیه و متن کامل مقاله در ادامه مطالب...